What is an enlarged prostate?
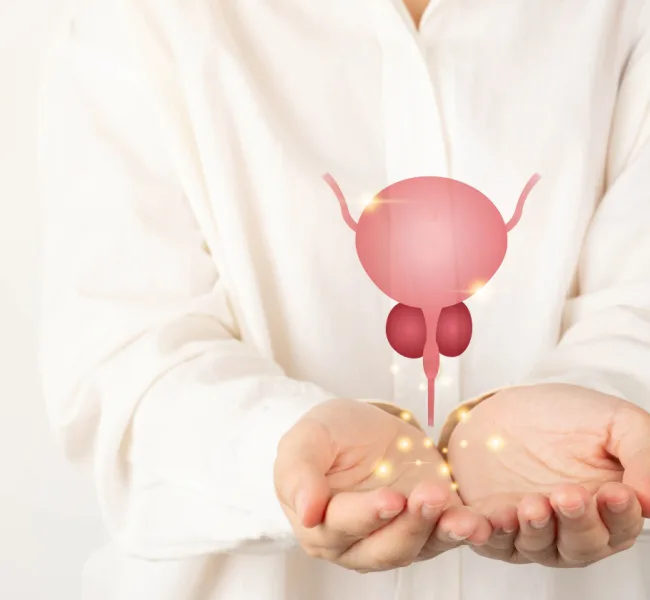
Enlarged prostate, also known as Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic obstruction is a medical condition in men, where the prostate gland gets enlarged. The prostate is a gland which helps in semen production, is situated beneath the bladder and frequently increases in size with age.
The prostate experiences two primary periods of growth as a man gets older. The initial phase happens during early puberty, resulting in a doubling of the prostate's size. The second phase of growth typically starts at around 25 years old and persists throughout most of a man's life, often coinciding with the occurrence of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
As the prostate grows larger, it applies pressure on and constricts the urethra. This action leads to thickening of the bladder wall. Over time, the bladder might lose strength and fail to completely expel urine, resulting in some remaining in the bladder. The constriction of the urethra and the difficulty in fully emptying the bladder are the primary issues linked with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
BPH has been categorized into 4 stages:
- Stage I: A patient without significant blockage or troublesome symptoms.
- Stage II: A patient experiencing troubling symptoms without significant blockage.
- Stage III: A patient experiencing significant obstruction, regardless of symptoms.
- Stage IV:A patient facing BPH complications like urine retention, recurring visible blood in urine, urinary infections, and the formation of bladder stones.