What are Uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are growths consisting of muscle and tissue that develop in or on the uterine wall. It might also develop in the fallopian tubes, cervix, or surrounding tissues near the uterus. These growths are the most frequent noncancerous (benign) tumor in women, and they almost never become cancerous. Uterine fibroids tend to be prevalent between the ages of 30 and the onset of menopause. Following menopause, they often undergo a reduction in size. The term leiomyosarcoma refers to a malignant fibroid. It is not more likely to develop a leiomyosarcoma if you already have fibroids. Fibroids are a prevalent form of growth, affecting around 40–80% of females.
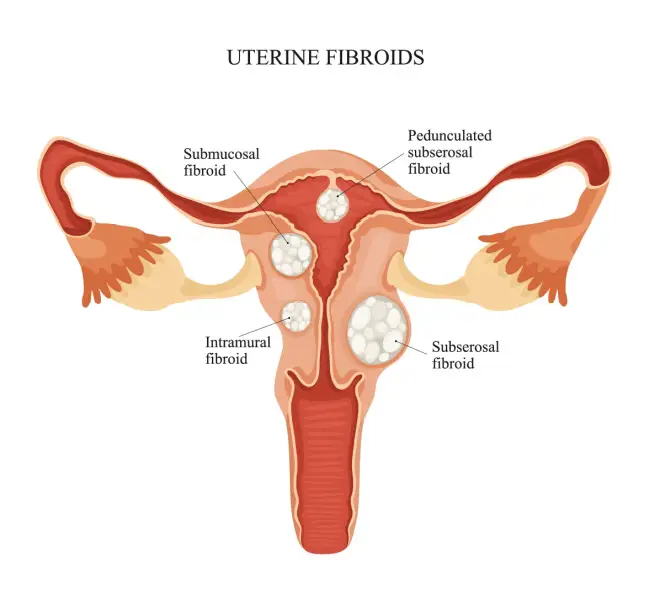
Fibroids have the potential to form either as clusters or as individual nodules. These clusters can vary significantly in diameter, ranging from as small as 1 millimeter to over 20 centimeters (8 inches) or even larger. Similarly, fibroids themselves can vary in size, ranging from as tiny as a seed to as large as a watermelon. These growths may develop on the exterior surface of the uterus, inside the main uterine cavity, or within the uterine wall.
A large-growing fibroid has the potential to deform the uterus both internally and externally. Certain fibroids can enlarge to the point where they fill the stomach or pelvis, in severe situations a person may appear pregnant. Uterine fibroids affect a lot of people at some point in their lives. However, since they frequently don't create any symptoms, patients might not be aware of it.